Introduction
One of the most important area in the day to day management of the firm is the management of working capital. Working Capital management is the functional area of finance that covers all the current account of the firm. It is concerned with the management of the level of individual current assets as well as the management of total working capital.
Working capital is described as the capital which is not fixed but the more common uses of the working capital are to consider it as the difference between the book value of current assets and current liabilities. We know that financial management means the procurement of funds and effective utilization of these procured funds.
Meaning and Definitions
“Working capital means current assets” According to Mead, Baker, and Malott,
“The sum of the current assets is the working capital of a business” J.S.Mill.
MEANING OF WORKING CAPITAL
Capital divided into two major headings.
 |
| CAPITAL |
Fixed capital means that capital, Fixed capital means which use for long period of time For example, Land, Building, Manufacturing Machinery and equipment, other equipment. purchase of permanent assets. Normally it consists of non-recurring in nature.
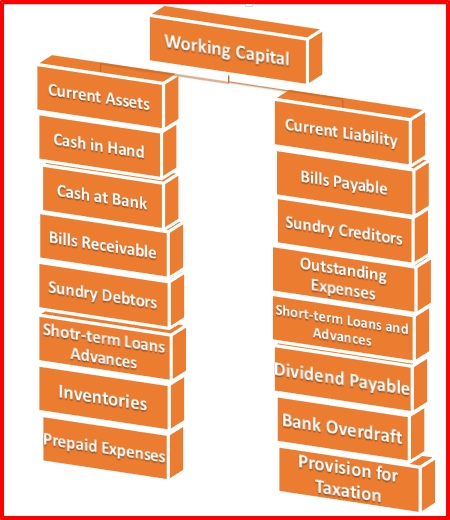
Working Capital is another part of the capital which is needed for meeting day to day requirement of the business concern. Working capital, also known as net working capital (NWC), is the difference between a company’s current assets, such as cash, accounts receivable (customers’ unpaid bills) and inventories of raw materials and finished goods, and its current liabilities, such as accounts payable. It can be easily converted into cash. Hence, it is also known as short-term capital.
Concept of Working Capital
 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Working Capital
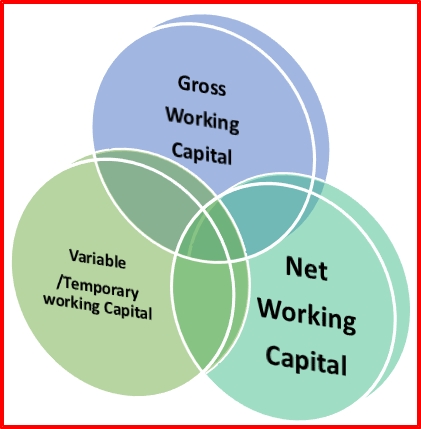
A.Gross Working Capital
It Simply Known as working capital which implies a total of all current assets Gross Working Capital is a general concept which determines the working capital concept. Thus the gross working capital is the capital invested in total current assets of the business concern.
GWC = Gross Working Capital,
CA = Current Assets
GWC = CA
B.Variable/Temporary working capital: That working capital is required to meet the seasonal demands special unforeseen events. The demands which are of seasonal nature require inventory. More adequate cash is required to overcome fluctuation in the market, to eliminate competition, etc.
C.Net Working Capital: Net Working Capital including Current Asset and Current Liability
Net Working Capital is the excess of current assets over the current liability of the concern during a particular period. If the current assets exceed the current liabilities it is said to be positive working capital; it is reversed, it is said to be Negative working capital.
NWC = C A – CL
TYPES OF WORKING CAPITAL
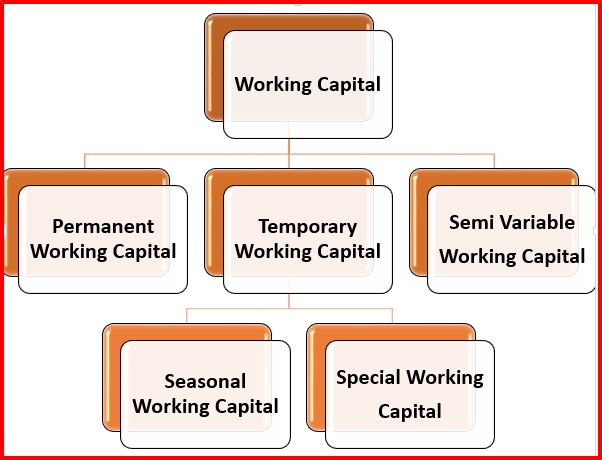
Working Capital may be classified into three important types on the basis of time
Permanent Working Capital
It is also known as Fixed Working Capital. It is the capital; the business concern must maintain a certain amount of capital at a minimum level at all times. The level of Permanent Capital depends upon the nature of the business. Permanent or Fixed Working Capital will not change irrespective of time or volume of sales.
Temporary Working Capital
It is also known as variable working capital. It is the amount of capital which is required to meet the Seasonal demands and some special purposes. It can be further classified into Seasonal Working Capital and Special Working Capital. The capital required to meet the seasonal needs of the business concern is called Seasonal Working Capital. The capital required to meet the special exigencies such as the launching of extensive marketing campaigns for conducting research, etc.
Semi-Variable Working Capital
A certain amount of Working Capital is in the field level up to a certain stage and after that, it will increase depending upon the change of sales or time.
Click on a link below to Read interesting topic English and Hindi
नीचे दिए गए लिंक पर क्लिक करें पढ़ें दिलचस्प विषय अंग्रेजी और हिंदी
1) Golden Rule of Accounting
2) | गोल्डन रूल्स ऑफ अकाउंटेंसी | लेखांकन के बेसिक नियम |
3) Material Telly.Erp9, How to create a Company in Telly.Erp9
4) TDS Rates / TDS Rate Chart for Financial Year 2018-19 or Assessment Year 2019-20, TCS RATE CHART FOR FY: 2018-19 (AY: 2019-20)
5) GST COMPUTATION & ACCOUNTING, What is GST Credit ?, Difference between GST Payable GST,IGST Tax Rate and Computation Credit?
6) What is GST in India? Goods & Services Tax Law Explained
भारत में GST क्या है? माल और सेवा कर कानून समझाया
7) Frequently Asked Questions On E-Way Bill
8) what are the objects of branch accounting
9) GST Rate reduced to 1% on affordable houses & 5% on others wef 01.04.2019
10) What is a Trademark? Trademark Registration in India: FAQs
11) Important amendment in Direct Tax for AY 2020-21
12) How To Compute Input Tax Credit Under GST
13) Note on the preparation of GST Annual Return in Form GSTR-9 at GSTN porta
14) Reverse Charge Mechanism (RCM) Under GST
15) Advance Tax – How to make Advance Tax Payment?
16) Key Highlights of CGST / IGST (Amendment) Act, 2018
17) Form GSTR-9 (GST annual return)- How to file with FAQs
18) What is Gratuity? How to calculate? Is Income Tax Exempted on Gratuity?
19) What are shares and dividend?
20) Income Tax, Under सेक्शन में कितना बचा सकते हैं टैक्स
21) Meaning and Natures of a company, Commentary on Section 168 of Companies Act, 2013
22) Mutual Fund
23) The concept of Share Capital, Small Shareholders’ Director Detail
24) Accounting For Managers, Accounting Process
25) What are the final accounts
27) Accounting For Managers, Basics of Accounting, Book-Keeping & Accountancy
28) Company secretary, Duties of company secretary, Right, and Power of the Company Secretary
29) Membership of the company, Right, Duties, Responsibility and their Termination
30) Company Meetings, Essentials of a valid meeting, Notice of the Meeting, SPECIMEN OF NOTICE:
31) What is Gratuity How to calculate? Is Income Tax Exempted on Gratuity?
ग्रेच्युटी क्या है? गणना कैसे करें? क्या ग्रेच्युटी पर आयकर छूट है?
33) Top 8 Ways To Start Investing Money
35) Financial Analysis
36) Income Tax, Under Taxes can save in the section
37) Financial Control
38) Digital Marketing
39) The Value of Money
40) Investment and Capital Structure Decision
41) long and short term financing
42) Valuation Bonds and stock
43) Capital Budgeting
44) Management And Estimation of Working Capital
45) FINANCIAL SYSTEM IN INDIA
46) Indian Insurance Sector
47) FINANCIAL MARKETS IN INDIA AND ROLE
48) Capital Market in India
49) EQUATED MONTHLY INSTALLMENTS (EMI)
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||









0 Comments