 |
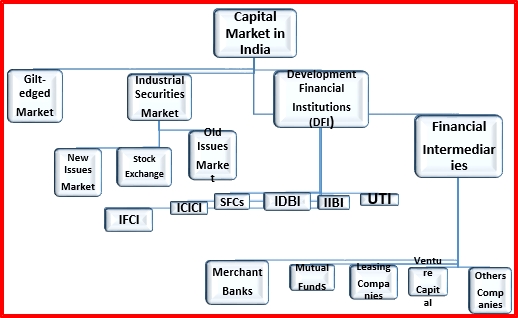
| Capital Market in India |
Market
for Government and semi-government securities, which carry fixed interest rates
and backed by RBI. The securities traded in this market are stable in value
and are much sought after by banks and other institutions.
The industrial securities market is the market for equities and debentures
of companies in the corporate sector. This market further classified into
(a)
New Issues Markets; for raising fresh capital in the form of shares and
debentures, and
(b)
Old Issues Market; for buying and selling shares and debentures of existing
companies–this market is commonly known as the stock market or stock exchange.
Both markets are equally important, but often the new issues market will be
facilitated only when there are abundant facilities for transfer of existing
securities. The capital market is also classified into Primary Capital Market
and Secondary Capital Market
The
primary capital market refers to the new issues market, which relates to
the issue of shares, preference shares and debentures of non-government public
limited companies, and also to the raising of fresh capital by Government
companies, and also to the raising of
fresh
capital by Government companies and the issue of public sector bonds.
The
secondary capital market, on the other hand, is the market for old or
already issued securities. It is composed of Industry Security Market or the stock exchange in where industrial securities are bought and sold, and the
Gilt-edged Market where the government and semi-government, securities are
traded.
Recommended for you Market Segmentation
Recommended for you Market Segmentation
A Development Finance Institution (DFI)
or Development Bank or Development Finance Company (DFC)
is a financial institution that provides risk capital for economic
development projects. They are often established by governments or charitable
institutions to provide funds to projects that would otherwise not be able to
get funds from commercial lenders. Some development banks include socially
responsible investing and impact investing criteria into their
mandates. Governments often use development banks to form part of their development
aid.
DFIs
can include multilateral development banks, bilateral development
banks, microfinance institutions, community development financial
institution and revolving loan funds
Mumbai Inter-Bank Offer Rate (MIBOR)
Mumbai Inter-Bank Bid Rate (MIBID)
MIBOR
and MIBID
On
June 15, 1998, the National Stock Exchange launched two new Reference Rates for the loans
of Inter-Bank Call Money Market. These rates are Mumbai Inter-Bank Offer Rate (MIBOR)
and Mumbai Inter-Bank Bid Rate (MIBID). MIBOR will be the indicator of Landing The rate for loans which MIBID will be the landing rate of receipts.
Share
Market
India has a well
developed a share market system, which is one of the best in the developing world.
It has one of the oldest stock markets in Asia. The first stock exchange was
established in 1875 in Bombay (Mumbai), when the stockbrokers against at their
plight following the severe depression insecurities decided to form an
association to protect the character and interest of native share and stock
brokers.
Primary
Market
The
primary market refers to the set up by which the industry raises funds by
issuing different types of securities. These securities are issued directly to
the investors, both individual and institutions. The primary market discharges
the important function of transfer of savings, especially of the individual,
Government and public sector undertakings. In the primary market, the new
issues of securities are presented in the form of Public issues, Right issues, and Private Placements. Its efficient operation is made possible by the financial
intermediaries and financial institutions, who arrange long-term financial transactions
for the clients. Issues of the securities in the primary market may be made through
(i) Prospectus, (ii) Offer for sale, and (iii)
Private Placement. The securities offered to the public through prospectus are
directly subscribed by the investor. The issuing companies widely publicize the
offer through various media. The Securities Exchange Board of India (SEBI) has
classified various issues in three groups i.e., New issues, Right issues, and Preferential issues. The SEBI has issued various guidelines regarding proper
disclosure for investor’s protection. These guidelines are required to be duly
observed by the companies making an issue of capital. The guidelines issued by the
SEBI broadly cover the requirements regarding the issue of capital by the companies.
The guidelines are applicable to all the companies after the repeal of
Controller of Capital Issues (CCI ) Act 1947.









0 Comments