A Financial System is a basic concept for the industrial development of the nation. Financial system provides an adequate and smooth flow of finance to the needed parts. It helps in the development and industrial work These parts are not always mutually exclusive; Inter-relationships between these are a part of the system e.g.. Financial Institutions operate in financial markets and are, therefore, a part of such markets. Indian financial system consists of four important components such as
• Financial Institutions
• Financial Markets
• Financial Instruments
• Financial Services.
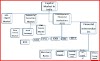
The Financial System implies a set of complex and closely connected or intermixed institutions, agent practices, markets, transactions, claims and liabilities in the economy. The Financial System is concerned with money, loan, and finance. A Financial System including Financial Institutions, Financial Market, Financial Services, Financial Instruments.
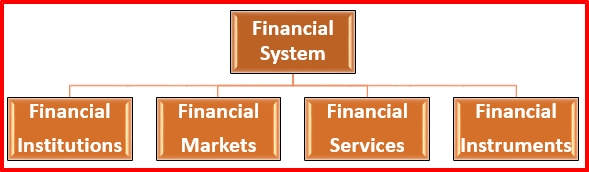 |
| Financial System |
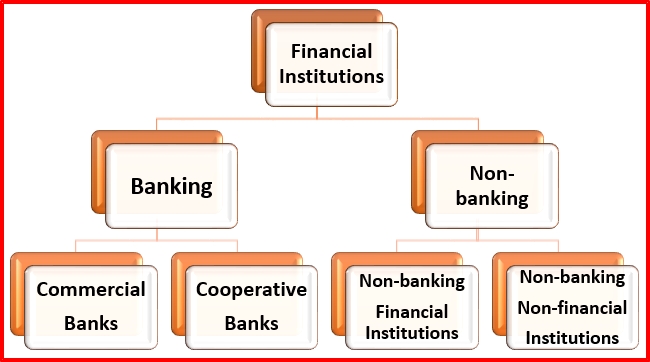
Financial Institutions
Financial institutions are the play a major role in the Indian Financial System.
Financial institutions are a major part of the Indian Financial System. Hence, it is more important than other components of the IFS because all the components of IFS are directly or indirectly related to the financial institutions. Financial institutions are providing various services to the economic development with the help of issuing of the financial instruments
.
Financial institutions, otherwise known as banking institutions, are corporations that provide services as intermediaries of financial markets. Broadly speaking, there are three major types of financial institutions
Financial institutions can be classified into banking and non-banking institutions. Now in India, all the financial institutions are systematically regulated and controlled by respective
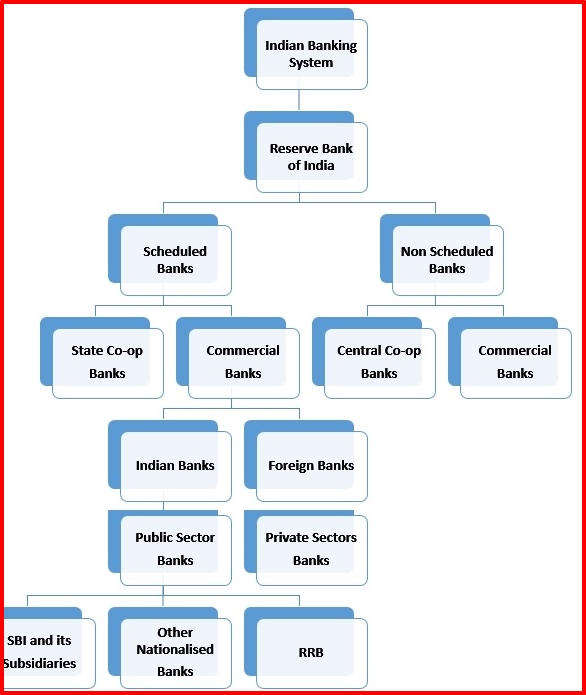
Banking Institutions
Banking Institutions are the Most important part for the development of Indians that providing various facilities of investment and loan that help in the development of India. Any country’s financial transaction should be properly arranged from investors to the needed industrialist. Banking institutions play a major role in the field of savings and investments of money from public and lending loans to the business concern.
Indian Banking institutions
(1) Commercial Banks (2) Cooperative Banks
Commercial Banks
Commercial Banks are the most important deposits mobilization and disbursers of finance. Indian commercial banks are the oldest, biggest and fastest growing financial institutions.
The main function of the commercial banks is accepting deposits and rendering loans to the public. Indian commercial banks can be classified into the following categories:
Nationalized Banks
To use financial institutions as the instrument of promoting economic and social development in a more purposeful manner and to overcome the monopoly over financial resources, the government of India nationalized 20 commercial banks during the tenure of Prime Minister of Indira Gandhi. On July 19, 1969.
1. Bank of India
2. Union Bank of India
3. Bank of Baroda
4. Bank of Maharashtra
5. Punjab National Bank
6. Indian Overseas Bank
7. Central Bank of India
8. Canara Bank
9. Syndicate Bank
10. Dena Bank
On April 15, 1980, the second nationalization took place with the following banks:
1. Andhra Bank
2. Corporation Bank
3. New Bank of India
4. Oriental Bank of Commerce
5. Punjab and Sind Bank
6. Vijaya Bank
State Bank of India (SBI)
The State Bank of India (SBI) is an Indian multinational, public Sector banking and financial services statutory body. It is a government corporation statutory body headquartered in Mumbai, Maharashtra. SBI is ranked as 216th in the Fortune Global 500list of the world's biggest corporations of 2018. It is the largest bank in India with a 23% market share in assets, besides a share of one-fourth of the total loan and deposits market
The largest Public sector bank of India which was created after the nationalization of Imperial Bank of India in 1955. It is now the largest commercial banks in India and in terms of branch largest in the world.
Private Sectors Banks
These comprise of foreign and private domestic banks. The foreign banks have a market share of % of total deposits into the banking industry and the domestic private banks have a share of 5.8% of total deposits of the banking industry.
Foreign Banks in India
RBI has been issuing licenses to various foreign banks to operate in India. More than 33 foreign and multinational banks are working in India today. The following are the major foreign banks play in Indian banking markets.
Non-banking Institutions
Apart from the banking institutions, Non-banking institutions are also performing their function to improve the Indian financial system. Non-banking Institutions can be classified into the following two major categories:
1. Non-banking Financial Institutions.
2. Non-banking Non-financial Institutions.
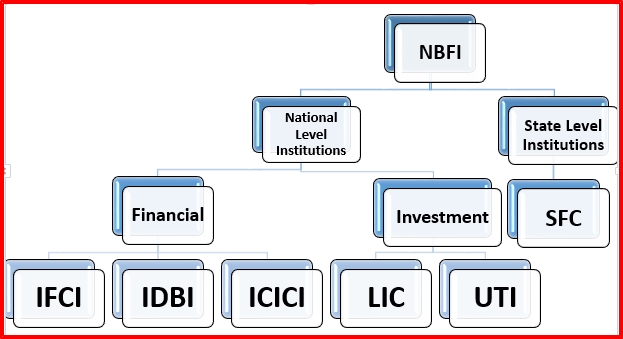
Non-banking Financial Institutions
Non-banking Financial Institutions are providing fund based services such as investment, insurance, mutual funds, and lending institutions:
Fig 4 Non-banking Financial Institutions
INDUSTRIAL FINANCE CORPORATION OF INDIA (IFCI)
Industrial Finance Corporation of India, the first development bank in India was set up on July 1, 1948 by passing a special Act as Industrial Finance Corporation of India Act 1948 in the parliament.
Insurance companies, investment trust, and co-operative banks. Industrial finance corporation of India can raise further capital with the help of issue of bonds, debentures, accepts deposits from public and advance from RBI.
Objectives
The objective of the Industrial finance corporation of India is to make medium and long-term credits more readily available to industrial concern in India, particularly to the industries.
• Manufacturing, preservation or procession of goods
• The mining industry
• The shipping industries
• The hotel industries
• Generation or distribution of electricity or power
INDUSTRIAL CREDIT AND INVESTMENT CORPORATION OF INDIA(ICICI)
Industrial Credit and Investment Corporation of India was started on January 5, 1955, as a Public Ltd. Companies under the companies act. It is only development bank which has participation by foreign investors.
Objective
The following are the major objectives of Industrial Credit and Investment Corporation of India:
1. To provide following are the major objectives of Industrial Credit and Investment Corporation of India:
2. To develop underwriting facilities, to help private sector units.
Functions
The main functions of the Industrial Credit and Investment Corporation of India are as
follows:
• Expansion of private sector industries.
• To give loans or guarantee of loans either in rupees or foreign currency.
• To underwrite shares and debentures and subscribes directory to share issued.
• To encourage and promote private capital.
• To promote private ownership of industrial investment along with the expansion of the investment market.
Management
Industrial Credit and Investment Corporation of India is managed by the board of directors which full-time chairman. The directors are nominated by Government, Reserve Bank of India Foreign shareholders and IDBI.
Subsidies of Industrial Credit and Investment Corporation of India
Industrial Credit and Investment Corporation of India is one of the leading and wide range of financial service providers in India. The following are the subsidies of the Industrial Credit and Investment Corporation of India.
• ICICI Banking Corporation Ltd.
• ICICI Securities and Finance Company Ltd.
• ICICI Assets Management Company Ltd.
• ICICI Trust Ltd.
• ICICI Brokerage Service Ltd.
• ICICI Credit Corporation Ltd.
INDUSTRIAL DEVELOPMENT BANK OF INDIA (IDBI)
The Industrial Development Bank of India was set up as a wholly owned subsidiary of the RBI on July 1st, 1964 under an act of parliament. In February 1976, it became an independent and autonomous bank.
Capital
Industrial Development Bank of India was started now it can raise further capital with the help of issue of shares, debentures and accept deposits from the public.
Objectives
The main objectives of the Industrial Development Bank of India are as follows:
• To provide credit, team finance, and financial services for the establishment of new projects.
• To expansion, diversification modernization and technology upgradation of existing Industrial concern.
• To provide several diversified financial products.
• To undertake merchant banking activities.
Functions
The functions of the Industrial Development Bank of India are as follows:
1. Direct finance: Project loan, soft loan, technical development loan, equipment
finance, etc.
2. Indirect finance: Refinancing, rediscounting of bills, seed capital to new entrepreneurs.
3. Special assistance: Promotion of development assistance funds.
4. General assistance: Non-financial promotional activities like marketing, research, consultancy, etc.
Subsidies of Industrial Development Bank of India are as follows:
• IDBI Bank Ltd.
• IDBI Capital Market Service Ltd.
• IDBI Mutual Funds.
• SIDBI
• IDBI Intech Ltd.
Industrial Development Bank of India has helped to set up the following institutions:
• Technical Consultancy Organization.
• EXIM Bank.
• Entrepreneurship Development Institute.
• Credit Rating and information service India Ltd.
INDUSTRIAL RECONSTRUCTION BANK OF INDIA (IRBI)
Origin
In April 1971, Industrial Reconstruction Corporation of India (IRCI) was set up by IDBI and other development and public sector banks. IRCI was reconstituted and renamed as Industrial Reconstruction Bank of India in 1985 with a special Act in the parliament.
Reserve Bank of India, SCB and various financial institutions. Further capital can be raised with the help of issue of shares, debentures and accept deposits from the public.
Objectives
Industrial Reconstruction Bank of India was established mainly for rehabilitating sick industrial units in India.
• To identify and remedial measures to sick industries.
• To provides financial assistance to the reconstruction of sick industrial units.
• To promote the sick units into profitable units.
Functions
The following are the major functions of the Industrial Reconstruction Bank of India Credit and reconstruction agency for industrial revival modernization, rehabilitation, expansion, reorganization, diversification, and rationalization. Empowered to grant loans and advances:
• Underwrite stocks, share, and bonds.
• Guarantee loans and advances, performances and deferred payments.
• Gives assistance for capital expenditure, the addition of balancing equipment, etc.
Subsidies of Industrial Reconstruction Bank of India
On March 27, 1997, Industrial Reconstruction Bank of India was transformed into Industrial Investment Bank of India Ltd (IIBI) under the Companies Act. IIBI acts as a coordinating agency in the field of reconstruction.
STATE FINANCE CORPORATION (SFC)
Central government decided to promote the Small Scale Industries and Medium Scale Industries at the state level by the establishment of State Finance Corporation under a special Act. It is called as State Finance Corporation Act 1951. According to this act, the state government has been empowered to set up State Finance Corporation. At present these
are 18 State Finance Corporation in India.
Schedule Commercial Bank, Reserve Bank of India and various financial institutions.
Objectives
• To provides financial assistance to Small scale industries
• To promote tiny, village and Cottage Industries
• To provide infrastructure facilities to SSI
Functions
• Long term loans to Small Scale Industries.
• Refinance from Reserve Bank of India and Industrial Development Bank of India
• Assistance from International Development Agency (IDA) and foreign currency hire of credit from the IDBI
STATE FINANCE CORPORATION IN TAMIL NADU
The Madras Industrial Investment Corporation (MIIC) was started as early as 1949, under the companies act and it was renamed as Tamil Nadu Industrial Investment Corporation (TIIC). It was the first State Finance Corporation in India, after the establishment of the State
Finance Corporation Act, 1951, the first State Finance Corporation was in Punjab in 1953.
EXPORT-IMPORT BANK (EXIM BANK)
EXIM bank was set up in January 1982 as a wholly owned by the central government.
It is empowered from RBI and also from central government to further capital raised by an issue of bonds and grants from the government.
Objectives
EXIM bank was established mainly for the purpose of promoting export and trading in India. The objectives are as follows:
• To promote the export and import activities
• To meet the financial requirements of the exporters
• To provide a guarantee and make foreign exchange facilities to exporters.
Functions
EXIM banks perform the following important functions:
1. Grants direct loans in India and outside for import and export.
2. Refinances loans and suppliers of credit.
3. Rediscounts usance export bills for banks.
4. Provides overseas investment finance.
5. Bulk import finance.
6. Foreign currency pre-shipment credit.
7. Product equipment finance programme.
8. Business advisory and technical assistance (BATA).
NATIONAL BANK FOR AGRICULTURAL AND RURAL DEVELOPMENT
Origin
The National Bank for agricultural and rural development was set up on July 12, 1982, based on the Recommendation of the All India rural credit survey committee under an act of Parliament as a central or apex institution for financing agricultural and rural sectors. It has taken over the functions of Agricultural Refinance and Development Corporation
(ARDC) and Agricultural credit department of Reserve Bank of India.
Further capital can be raised from the special borrowings from the Central Government.
Objectives
The main objectives of the National Bank for Agricultural and Rural Development are as follows:
• To provides refinance assistance for agriculture, Small Scale Industries, and Village Industries.
• To undertakes promotional activities for integrated rural development
• To coordinates agricultural finance along with the state government
• To undertakes research and development in agriculture, rural industries
Functions
The National Bank for agricultural and rural development discharges are:
It provides all sorts of reference to Co-operatives, Commercial Banks, and Regional Rural Banks, in respect to the above three agencies and advice the government thereon. It makes loans to the state government to enable them to subscribe to the share capital of the co-operative bank.
It helps in promoting research in agriculture and rural development. National bank for agricultural and rural development undertakes evaluation and monitoring projects financed by it. It is responsible for the development, operation, and co-ordination relating to rural credit.
SPECIALIZED FINANCIAL INSTITUTIONS
The following are the specialized financial institutions established by the government to provide financial and non–financial assistance to various industrial sectors in India.
• Shipping Credit and Investment Corporation of India (SCICI), 1986.
• Infrastructure Leasing and Financial Service Limited (IL and FS), 1988.
• Technology Development and Information Company of India Limited (TDICI),
1988.
• Risk Capital and Technology Finance Corporation Limited (RCTFC), 1988.
• Tourism Finance Corporation of India (TFCI), 1989.
• Small Industries Development Bank of India (SIDBI), 1989.
• Infrastructure Development Finance Company (IDFC), 1997.
INSURANCE SECTOR IN INDIA
Insurance is one of the funds based financial services which provides risk coverage facilities to human beings. Realising the vast potential in Indian market, foreign insurance companies started entering into India and even banking organizations (SBI, ICICI, etc.) also showed much interest in insurance business, this is being attributed to global technology
and conversions of services as a result of which Indian Insurance market registered the highest growth in the Asian region even though Indian’s share of global insurance premium is less 0.5% (1998) than that of US 24.2 percent and Japan 21 percent. The private players from India and abroad are well aware that only 25 percent of the insurable population have been covered by insurance by existing companies which includes that the Indian insurance market has potential enough to exploit. In this process, IRDA has so for granted registration for 12 private life insurance companies and 9 general insurance. If the existing public sector insurance companies are included, there are about 14 insurance companies in the life side and 13 companies in the general insurance business. Insurance sectors in India have been classified into the following categories: That show in Next Post
Click on a link below to Read interesting topic English and Hindi
दिलचस्प विषय अंग्रेजी और हिंदी
1) Golden Rule of Accounting
2) | गोल्डन रूल्स ऑफ अकाउंटेंसी | लेखांकन के बेसिक नियम |
3) Material Telly.Erp9, How to create a Company in Telly.Erp9
4) TDS Rates / TDS Rate Chart for Financial Year 2018-19 or Assessment Year 2019-20, TCS RATE CHART FOR FY: 2018-19 (AY: 2019-20)
5) GST COMPUTATION & ACCOUNTING, What is GST Credit ?, Difference between GST Payable GST,IGST Tax Rate and Computation Credit?
6) What is GST in India? Goods & Services Tax Law Explained
भारत में GST क्या है? माल और सेवा कर कानून समझाया
7) Frequently Asked Questions On E-Way Bill
8) what are the objects of branch accounting
9) GST Rate reduced to 1% on affordable houses & 5% on others wef 01.04.2019
10) What is a Trademark ? Trademark Registration in India: FAQs
11) Important amendment in Direct Tax for AY 2020-21
12) How To Compute Input Tax Credit Under GST
13) Note on the preparation of GST Annual Return in Form GSTR-9 at GSTN porta
14) Reverse Charge Mechanism (RCM) Under GST
15) Advance Tax – How to make Advance Tax Payment?
16) Key Highlights of CGST / IGST (Amendment) Act, 2018
17) Form GSTR-9 (GST annual return)- How to file with FAQs
18) What is Gratuity? How to calculate? Is Income Tax Exempted on Gratuity?
19) What are shares and dividend?
20) Income Tax, Under सेक्शन में कितना बचा सकते हैं टैक्स
21) Meaning and Natures of a company, Commentary on Section 168 of Companies Act, 2013
22) Mutual Fund
23) The concept of Share Capital, Small Shareholders’ Director Detail
24) Accounting For Managers, Accounting Process
25) What are the final accounts
27) Accounting For Managers, Basics of Accounting, Book-Keeping & Accountancy
28) Company secretary, Duties of company secretary, Right, and Power of the Company Secretary
29) Membership of the company, Right, Duties, Responsibility and their Termination
30) Company Meetings, Essentials of a valid meeting, Notice of the Meeting, SPECIMEN OF NOTICE:
31) What is Gratuity How to calculate? Is Income Tax Exempted on Gratuity?
ग्रेच्युटी क्या है? गणना कैसे करें? क्या ग्रेच्युटी पर आयकर छूट है?
33) Top 8 Ways To Start Investing Money
35) Financial Analysis
36) Income Tax, Under Taxes can save in the section
37) Financial Control
38) Digital Marketing
39) The Value of Money
40) Investment and Capital Structure Decision
41) long and short term financing
42) Valuation Bonds and stock
43) Capital Budgeting
44) Management And Estimation of Working Capital
45) FINANCIAL SYSTEM IN INDIA
46) Indian Insurance Sector
47) FINANCIAL MARKETS IN INDIA AND ROLE
48) Capital Market in India
49) EQUATED MONTHLY INSTALLMENTS (EMI)








0 Comments